Medically Reviewed by: Dr. Erin Scheidemann, PhD | October 7th, 2025
Peritoneal mesothelioma affects the peritoneum (the lining of the abdominal cavity). It’s rare, accounting for only about 20 percent of all mesothelioma cases annually, or about 660 cases per year in the United States. Patients with peritoneal mesothelioma may have a better prognosis than those with other types of mesothelioma. Typically, treatment involves a combination of chemotherapy and surgery.
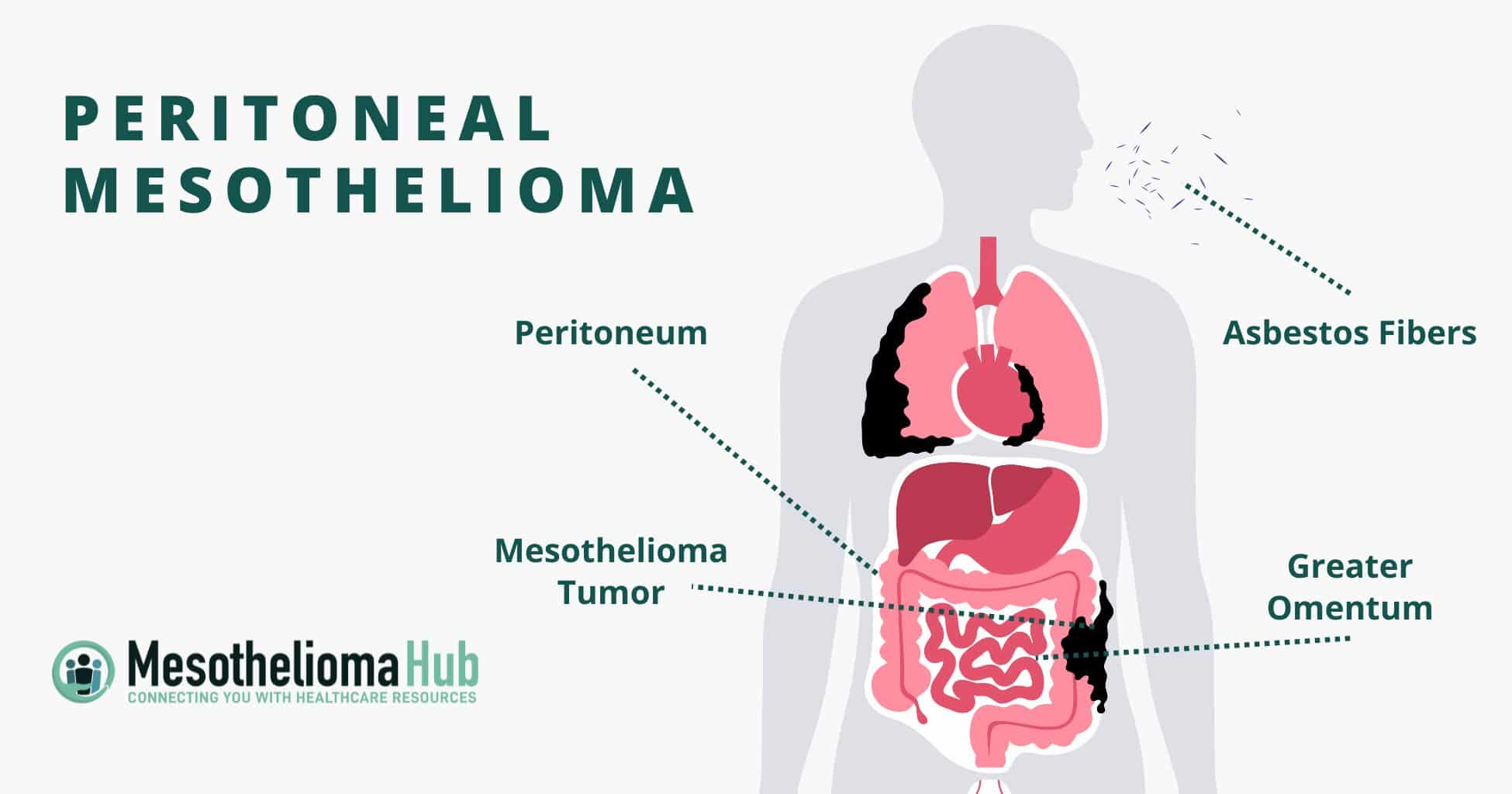
Peritoneal mesothelioma usually develops due to asbestos exposure. Asbestos, a cancer-causing mineral, has been used in both commercial and residential applications for decades. Because asbestos fibers can travel for miles by becoming airborne and be transported on the clothing, skin, or hair, meaning even those living with people who are exposed to asbestos at work are at risk.
Asbestos fibers can be swallowed or inhaled, traveling to the abdominal cavity, where they harm cells over time. The length of the latency period depends on how much asbestos you were exposed to and how long the exposure was. It can take up to 40 years before symptoms develop, a period known as the latency period. Between the initial asbestos exposure and the first sign of symptoms, your cells can become so damaged that cancer slowly starts to form. The cancer can grow and spread before you notice any symptoms. When symptoms are noticed, it’s often been such a long time from asbestos exposure that they aren’t linked, which delays diagnosis. Because of this delay, many people aren’t diagnosed until the disease is in an advanced stage. Early detection is critical as patients who identify symptoms sooner have more treatment options and often better outcomes.
Understanding the causes and symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and treatment planning. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what symptoms to watch for, how peritoneal mesothelioma is diagnosed, available treatment options, and how to connect with specialists who can provide the best possible care.
All forms of mesothelioma take years to manifest. During the latency period, the asbestos fibers become embedded in the body and cause damage. Over time, this damage slowly gets worse and can move to other nearby organs. By the time symptoms appear, the disease has likely advanced or spread.
Diagnosis starts with imaging such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. If fluids (ascites) are present in the abdomen, doctors may also take samples (paracentesis) for analysis or fluid biopsies. A tissue biopsy is often the last step in the process and is the only definitive way to diagnose the cancer type. Biopsies show what cell type the tumor is made of, which is important information when deciding on a treatment plan. Common biopsies for diagnosing peritoneal mesothelioma include:
Peritoneal mesothelioma is most often diagnosed at specialized care centers where teams of oncologists, pathologists, and surgeons work together to ensure accurate results.
Peritoneal mesothelioma can be difficult to diagnose because it’s rare and symptoms overlap with common conditions. Some conditions cause nonspecific symptoms, such as abdominal pain, swelling, or digestive changes, similar to those associated with peritoneal mesothelioma. Common misdiagnoses include:
Because of these similarities, many patients experience delays in receiving the correct diagnosis. Seeking care from a specialist is important because they have the necessary experience to distinguish between peritoneal mesothelioma and other conditions and recommend the appropriate treatment.
At first, symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma can include abdominal discomfort and pain. Over time, these can progress to more severe symptoms like unexplained weight loss and abdominal distension. Additional symptoms include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, talk to your healthcare provider. Inform your doctor if you may have been exposed to asbestos at work or indirectly.
The Peritoneal Cancer Index (PCI) was first developed as a research tool to predict cancer severity. It has since become the standard method to stage peritoneal mesothelioma.
The PCI divides the abdomen into 13 sections. Each section is given a number from zero to three based on how much cancer is seen. Zero indicates no cancer, and three means that the entire section has cancer. All scores are added, which determines cancer stage:
The score helps doctors determine treatment options. A low score indicates that more aggressive treatments might work for you.
While this cancer is aggressive, it’s not always immediately fatal. Prognosis depends on factors like stage, patient age, and overall health. Early detection and access to advanced treatment are important because they can improve survival and life expectancy.
Patients treated with cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC (see below) can live for between two and six years. Clinical trials are currently testing immunotherapy and targeted treatments. These advancements provide hope for longer survival and improved quality of life.
The most common treatment plan for peritoneal mesothelioma is peritonectomy. This procedure can completely remove the cancer or help alleviate pain to improve quality of life (palliative care). It combines cytoreductive surgery (surgery to remove all visible tumors) with heated chemotherapy, called HIPEC (hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy).
In this procedure, the surgeon removes the lining of the abdomen and all tumors. A heated chemotherapy wash then removes remaining cancerous cells. Because the chemotherapy is localized, a higher dose can be directly applied to the affected area without damaging other organs.
Because peritoneal mesothelioma is a rare condition, selecting a treatment team with experience is crucial. Specialists at top centers provide access to surgery, HIPEC, clinical trials, targeted therapies, and palliative care.
Some of the renowned cancer centers that specialize in peritoneal mesothelioma treatment include:
We can also help patients and families connect with both medical experts and legal professionals. This ensures patients get the right treatment while also pursuing compensation for asbestos-related exposure, which can help cover medical costs.
Our team of authors collaborates with the advocate team, focusing on writing about asbestos exposure and mesothelioma to spread awareness. They are dedicated to supporting families within the mesothelioma community.

Erin earned a Bachelor of Science in Biology from The College of New Jersey in 2020 and a Doctor of Philosophy in Tumor Biology from Georgetown University in 2024. Erin is passionate about making health information accessible and informing people about the latest research that can impact their lives.
American Journal of Case Reports. (2025). Delayed Diagnosis of Peritoneal Mesothelioma in Recurrent Ascites: A Case Report. Retrieved on September 20, 2025 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11991405/
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics. (2022). The Importance of the Peritoneal Cancer Index (PCI) to Predict Surgical Outcome After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Advanced Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9519707/
Cancer. (2022). Malignant Mesothelioma: Advances in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Mesothelin Targeted Therapies. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8555868/
Cleveland Clinic. (2022). Peritoneal Mesothelioma. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23973-peritoneal-mesothelioma
MedStar Health. (2025). Peritoneal Cancer Care: Advanced Treatment and Hope. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://www.medstarhealth.org/services/peritoneal-surface-malignancy-program
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. (2025). Mesothelioma Diagnosis. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://mskcc.org/cancer-care/types/mesothelioma/diagnosis
Penn Medicine. (2025). Mesothelioma Diagnosis and Staging. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://pennmedicine.org/conditions/mesothelioma/diagnosis
Rutgers Cancer Institute. (2025). Peritoneal Mesothelioma: What Is It? Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://cinj.org/peritoneal-mesothelioma-what-it
StatPearls. (2023). Laparotomy. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525961/
StatPearls. (2023) Paracentesis. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK435998/
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. (2025). 6 Innovative Mesothelioma Treatment Options. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://mdanderson.org/cancer-types/mesothelioma/mesothelioma-treatment.html
University of Maryland School of Medicine. (2025). Mesothelioma Treatment & Research Program. Retrieved on September 20, 2025, https://www.medschool.umaryland.edu/surgery/divisions/